Introduction to Landguard Raised Beds
Gardening enthusiasts are always on the lookout for methods that can enhance their gardening experience and improve productivity. One such effective method is the use of raised garden beds. Among various options in the market, landguard raised beds stand out as an excellent choice, offering a blend of functionality, durability, and aesthetic appeal. These beds are specifically designed to elevate the planting surface, provide enhanced soil conditions, and allow for easier gardening practices. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what raised beds are, their benefits, how to design your garden using landguard raised beds, step-by-step building instructions, and tips for growing and maximizing productivity in your raised beds.
What Are Raised Beds?
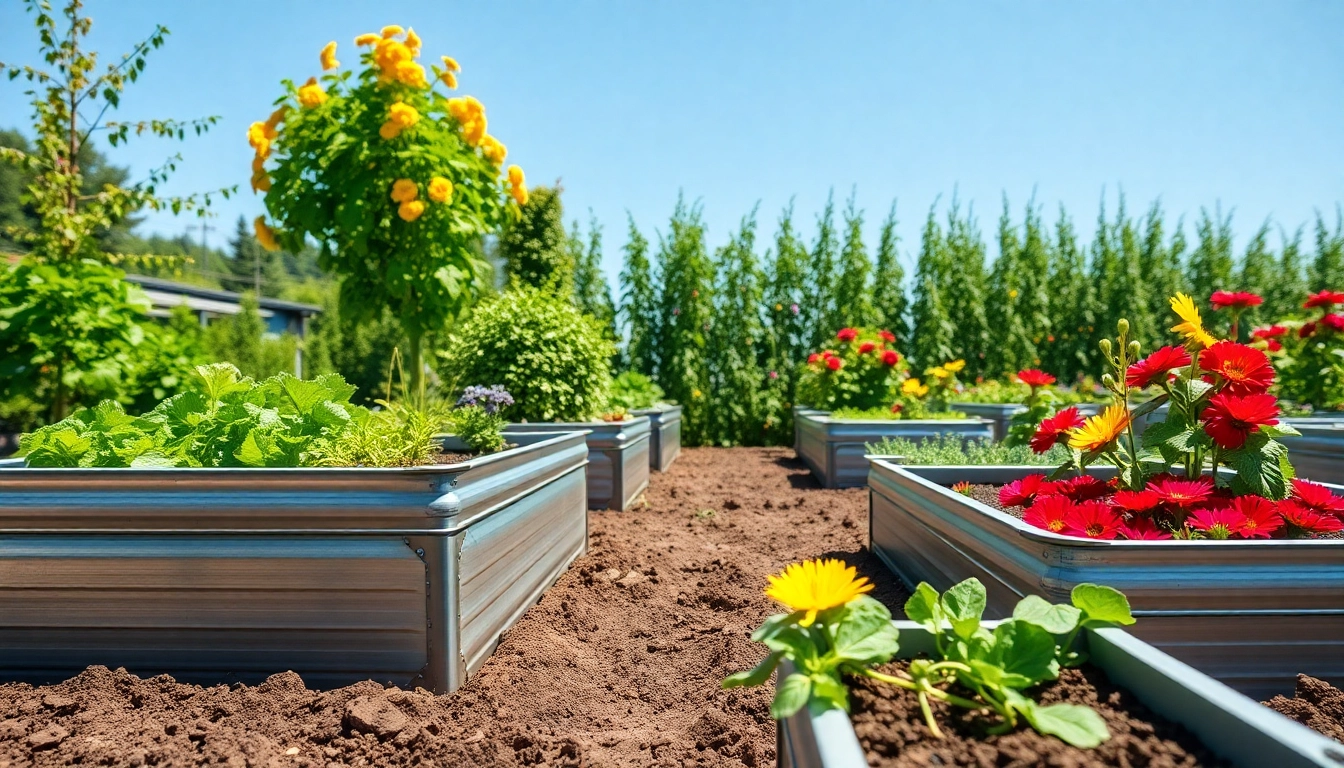
Raised garden beds are garden plots that are built above the surrounding soil level, often framed with wood, brick, stone, or metal. They are typically filled with a specialized soil mix, allowing for improved drainage, soil aeration, and easy access for planting and maintenance. The height of raised beds can vary, catering to different gardening needs—from low beds designed for a variety of vegetables to taller options suitable for those who may have difficulty bending down.
Benefits of Using Landguard Raised Beds
There are multiple advantages to using raised beds in your gardening endeavors. Some key benefits of landguard raised beds include:
- Improved Soil Quality: By filling raised beds with the right soil mix, you can create optimal conditions for plant growth––leading to better yields.
- Better Drainage: Raised beds offer superior drainage capabilities, eliminating waterlogged conditions that can damage plant roots.
- Enhanced Accessibility: The elevation of beds improves accessibility for individuals with mobility challenges, making gardening easier.
- Weed and Pest Control: With raised beds, controlling weeds becomes simpler, and many common pests can be deterred.
- Extended Growing Season: The soil warms up earlier in spring and retains heat longer in fall, allowing more extended periods for plant growth.
Choosing the Right Size for Your Garden
When selecting the size of your landguard raised beds, a few considerations come into play:
- Available Space: Evaluate your available outdoor space to determine how large your beds can be. You want to optimize the area without overcrowding your garden.
- Gardening Goals: Consider what you plan to grow. Different plants have unique space requirements that influence bed size.
- Accessibility: Ensure that the beds are appropriately sized to allow comfortable access from both sides, especially if they are wider.
Designing Your Garden with Landguard Raised Beds
Effective garden design is crucial for maximizing the potential of your raised beds. A well-thought-out layout takes into account plant compatibility, growth habits, and aesthetic appeal.
Planning Your Layout
The first step in designing your garden is to create a layout. Consider the following tips:
- Grid Layout: A grid system helps in organizing your plants efficiently, often allowing for row planting.
- Pathways: Leave enough space between beds to create access pathways for easy movement. This not only helps with maintenance but also adds to the overall aesthetics.
- Sunlight Exposure: Place taller plants on the north or west side of the garden bed to prevent overshadowing shorter plants.
Soil and Drainage Considerations
Soil quality is paramount in the success of raised bed gardening. A blend of organic compost, peat moss, and local soil can create the ideal planting medium. Ensure that the soil is:
- Well-draining: Adequate drainage is crucial to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot.
- Nutrient-rich: Incorporate organic fertilizers and compost to provide nutrients to your plants.
- Aerated: Proper aeration allows roots to breathe and promotes healthy growth.
Incorporating Companion Planting Techniques
Companion planting can enhance growth and deter pests naturally. Some beneficial combinations include:
- Tomatoes and Basil: These two plants benefit one another, enhancing flavor and growth.
- Carrots and Onions: This duo can help repel pests associated with each plant.
- Beans and Corn: Beans fix nitrogen in the soil, benefiting corn, while the corn provides support for the beans to climb.
Building Your Landguard Raised Beds
Constructing your landguard raised beds is a rewarding project. With the right materials and a clear plan, anyone can build their own raised beds.
Materials Needed for Construction
Gather the following materials to construct your landguard raised beds:
- Wood or metal boards for the frame
- Wooden stakes for stability
- Soil mix (including compost and organic matter)
- Drilling tools and screws (if using wood)
- Landscape fabric (to line the base if necessary)
Step-by-Step Assembly Instructions
Follow these steps to assemble your landguard raised beds:
- Determine the location: Pick a sunny spot and mark out the dimensions of your bed.
- Cut the materials: Measure and cut the wood or metal sheets to create the frame.
- Assemble the frame: Join the corners using screws or brackets for stability.
- Secure the frame to the ground: Use stakes at the corners or sides for stability.
- Fill with soil: Layer the soil mix into the bed, creating a mound in the center to facilitate drainage.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
To ensure the longevity of your raised beds:
- Regularly check for rot: Use rot-resistant materials to extend the life of wooden beds.
- Clear debris: Keep the area around the beds clear to minimize pests.
- Refresh the soil: Top up with soil or compost each season to maintain nutrient levels.
Growing in Landguard Raised Beds
With your raised beds in place, it’s time to start planting. A well-maintained bed can be the perfect environment for a variety of plants.
Ideal Plants for Raised Bed Gardening
Several plants thrive in raised beds, including:
- Vegetables: Carrots, radishes, and salad greens grow well in the nutrient-rich environment.
- Herbs: Basil, cilantro, and parsley flourish and are highly sought after for culinary usage.
- Flowers: Marigolds and nasturtiums can attract beneficial insects while also adding charm to the garden.
Watering and Fertilization Strategies
Proper watering techniques are vital to the success of your plants in raised beds:
- Consistent Moisture: Raised beds can dry out faster than traditional gardens, so consistent moisture levels are essential.
- Drip Irrigation: Consider installing a drip system for efficient watering.
- Organic Fertilizers: Use compost or organic fertilizers to enrich the soil during the growing season.
Pest Control in Raised Beds
Managing pests organically in your raised beds can be achieved through various strategies:
- Physical Barriers: Use nets or row covers to protect young plants from pests.
- Natural Predators: Encourage birds and beneficial insects to control pest populations naturally.
- Regular Inspections: Frequently check plants for signs of pests and act quickly to mitigate damage.
Maximizing Productivity with Landguard Raised Beds
To make the most out of your landguard raised beds, consider implementing strategic practices that enhance productivity.
Seasonal Planting Guide
Different plants thrive at various times of the year. A seasonal planting guide can help you schedule what to plant when. Some examples include:
- Spring: Start cool-season crops like lettuce and peas.
- Summer: Transition to warm-season crops such as tomatoes and peppers.
- Fall: Consider planting fall crops, including kale and Brussels sprouts.
Implementing Crop Rotation
Crop rotation helps prevent soil degradation and pest populations:
- Plan rotation schedules: Change plant families each season to disrupt pest cycles.
- Build soil health: Alternate between heavy feeders, light feeders, and legumes to ensure soil nutrient balance.
Harvesting and Storing Your Produce
Once your plants are ready to be harvested, proper techniques will mitigate spoilage:
- Harvest at the right time: Every plant has a peak time for harvesting; for instance, tomatoes should be picked when fully ripe.
- Store correctly: Ensure vegetables are stored in appropriate conditions to prolong freshness.
In conclusion, embracing the use of landguard raised beds not only enhances your gardening experience but also paves the way for achieving a flourishing garden. By understanding the fundamental principles of raised bed gardening, from layout planning to plant selection and care, you can elevate your gardening outcomes significantly. With consistent care and knowledgeable practices, the landguard raised beds in your garden can become a thriving ecosystem that brings joy and productivity season after season.